Displacement Current and Maxwell's Equations
Displacement Current and Maxwell's Equations: Overview
This topic explains the concept of displacement current. It discusses Maxwell's equations. It describes Gauss's law of electricity and magnetism, Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction, and Ampere-Maxwell's circuital law.
Important Questions on Displacement Current and Maxwell's Equations
Mark the correct statement :-
(1) Displacement current is produced only by varying magnetic field.
(2) Displacement current is produced by varying electric field only.
(3) Displacement current is produced by varying electric field as well as varying magnetic field.
(4) Displacement current can be produced neither by varying electric field nor by varying magnetic field.
Which of the following Maxwell’s equation is valid for time varying conditions but not valid for static conditions:
Who proposed the electromagnetic theory of light?
The source of displacement current is _____
A parallel plate capacitor has two circular plates of radius each, separated by a distance . The magnitude of the instantaneous electric field between the plates is given by , where and are positive constants. A positive value of corresponds to the upward direction as shown in the figure.
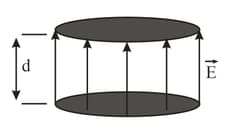
At , the displacement current between the plates is
A long wire of radius is made of two different metals, depositing one metal over the other. The inner core occupies the region and the outer region . Because of difference in the conductivity of the two wires, only of the total current flows through the inner core and the balance through the second metal. The current density in each metal is constant.
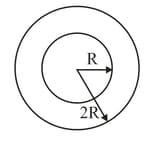
The magnetic field at a distance from the centre is
A parallel plate capacitor with plates of side and plate separation is being charged by an external emf Volts. The displacement current (in Amperes) in the capacitor is
A parallel plate capacitor of plate dimensions is being charged by a current of In the region between the plates, the charging current produces a uniform electric field perpendicular to the plates. The rate of change of the electric field strength with time is
An electric field changing with time gives rise to a magnetic field, is a consequence of the _____ being a source of magnetic field.
List the consequences of the displacement current.
Which of these is a correct definition of conventional current?
Displacement current is continuous:
Ampere's circuital law is given by:
Define ampere circuital law.
What is conventional electric current?
According to Maxwell's hypothesis, a changing electric field give rise to
The charge of a parallel plate capacitor is varying as . The plates are very large and close together (area, separation). Neglecting the edge effects, the displacement current through the capacitor is
Instantaneous displacement current of in the space between the parallel plate of capacitor can be established by changing potential difference at a rate of
If the magnetic monopole exists, then which of the Maxwell’s equation has to be modified?
The net magnetic flux of a magnetic field passing through a closed surface is
